Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 3(111) and
3(111) and  5(0-13) grain boundaries of
5(0-13) grain boundaries of  -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Metals, 12(4), p.662_1 - 662_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.25(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Phosphorus atoms in steels accumulate at grain boundaries via thermal and/or irradiation effects and induce grain boundary embrittlement. Quantitative prediction of phosphorus segregation at grain boundaries under various temperature and irradiation conditions is therefore essential for preventing embrittlement. To develop a model of grain boundary phosphorus segregation in  -iron, we studied the migration of a phosphorus atom in two types of symmetrical tilt grain boundaries (
-iron, we studied the migration of a phosphorus atom in two types of symmetrical tilt grain boundaries ( 3[1-10](111) and
3[1-10](111) and  5[100](0-13) grain boundaries) using molecular dynamics simulations with an embedded atom method potential. The results revealed that, in the
5[100](0-13) grain boundaries) using molecular dynamics simulations with an embedded atom method potential. The results revealed that, in the  3 grain boundary, phosphorus atoms migrate three-dimensionally mainly in the form of interstitial atoms, whereas in the
3 grain boundary, phosphorus atoms migrate three-dimensionally mainly in the form of interstitial atoms, whereas in the  5 grain boundary, these atoms migrate one-dimensionally mainly via vacancy-atom exchanges. Moreover, de-trapping of phosphorus atoms and vacancies was investigated.
5 grain boundary, these atoms migrate one-dimensionally mainly via vacancy-atom exchanges. Moreover, de-trapping of phosphorus atoms and vacancies was investigated.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
JAEA-Conf 2017-001, p.91 - 96, 2018/01
Toward evaluation of deuteron nuclear data, we have been developing a code system dedicated for the deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. In the present work, we make an improvement in DEURACS and apply it to composite-particle emission from deuteron-induced reactions. The calculation using DEURACS reproduces the experimental double-differential cross sections of 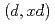 ,
, 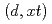 ,
, 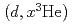 , and
, and 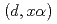 reactions on
reactions on  Al and
Al and  Ni at incident energy of 80 MeV quantitatively well. From the results of the analyses, it is shown that the treatment of inelastic scattering and pick-up reaction processes is important in the calculation of deuteron-induced composite-particle emission.
Ni at incident energy of 80 MeV quantitatively well. From the results of the analyses, it is shown that the treatment of inelastic scattering and pick-up reaction processes is important in the calculation of deuteron-induced composite-particle emission.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.12025_1 - 12025_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:90.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recently, intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerator have been proposed for various applications. Accurate and comprehensive deuteron nuclear data library over wide ranges of target mass number and incident energy are indispensable for the design of deuteron accelerator neutron sources. Thus, we have developed an integrated code system dedicated for analysis and prediction of deuteron-induced reactions, which is called DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS). In the present work, the analysis of  reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to
reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to 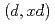 reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the
reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the  and
and 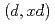 reactions well.
reactions well.
 -Iron Using First-Principles-Based Kinetic Monte Carlo
-Iron Using First-Principles-Based Kinetic Monte CarloEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Yamaguchi, Masatake
Materials Transactions, 58(1), p.26 - 32, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:38.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to evaluate grain boundary (GB) phosphorous (P) segregation in nuclear reactor pressure vessel steels under irradiation, the rate-theory model based on first-principles calculations is developed. In this study, we evaluated the diffusion coefficient of the mixed interstitial dumbbell of a P atom and an iron(Fe) atom using a kinetic Monte Carlo (kMC) simulation based on first-principles calculations. The evaluated diffusion coefficient was almost the same with the diffusion coefficient of P atoms which migrate via octahedral interstitial sites, and was much faster than that for P transport by vacancies. Furthermore, from the simulation of the irradiation induced GB P segregation using the model which was modified to include P atoms of octahedral interstitial sites, it was found that the boundary condition at GB is not valid for P atoms of octahedral interstitial sites
 reactions on beryllium
reactions on berylliumKono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.165 - 170, 2016/09
For engineering design of deuteron accelerator neutron sources, accurate nuclear data of deuteron-induced reactions on neutron converter (Li, Be, C, etc.) and accelerator structure material (Fe, Cr, Ni, etc.) are indispensable. Therefore we have developed a computational code system based on physics models dedicated for deuteron nuclear data evaluation. In the present study, we have analyzed the  reactions on beryllium at incident deuteron energies up to 65 MeV. Since there is a lot of experimental Thick Target Neutron Yields (TTNYs), double-differential
reactions on beryllium at incident deuteron energies up to 65 MeV. Since there is a lot of experimental Thick Target Neutron Yields (TTNYs), double-differential  cross sections are calculated by the code system and then are converted to TTNYs. It is found that the calculated TTNYs reproduce the experimental ones fairly well except in the low neutron energy region.
cross sections are calculated by the code system and then are converted to TTNYs. It is found that the calculated TTNYs reproduce the experimental ones fairly well except in the low neutron energy region.
 reactions on
reactions on  Be and
Be and  C at incident energies up to 50 MeV
C at incident energies up to 50 MeVNakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
Physical Review C, 94(1), p.014618_1 - 014618_9, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:89.9(Physics, Nuclear)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) from deuteron bombardment on thick Be and C targets are analyzed using the DEURACS (DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System). The calculated TTNYs reproduced the experimental ones quantitatively well in the incident energy range up to 50 MeV. In addition, it was found that the proton stripping reaction makes the most dominant contribution to neutron production. From the analysis, we conclude that the DEURACS is applicable to  reactions and modeling of the stripping reaction is essential to predict neutron production yields accurately.
reactions and modeling of the stripping reaction is essential to predict neutron production yields accurately.
Kishimoto, Maki; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Sakasai, Kaoru; Katagiri, Masaki; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Nakazawa, Masaharu*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 43(2), p.168 - 181, 2001/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 C
CB.J.Marsden*; ; R.Charles*
Proc. of meeting: Open Discussion on Current Issues in Nuclear Graphite and Carbon Topics, 0, 1 Pages, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Ebihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Nishiyama, Yutaka
no journal, ,
Since grain-boundary (GB) embrittlement by phosphorus (P) under irradiation is a crucial problem in steels, it is necessary to evaluate irradiation-induced P GB segregation in order to secure the integrity of nuclear structural materials. Recently, partial diffusion coefficients including the vacancy (V) drag effect, which are obtained by the kinetic Monte Carlo method incorporating the barrier energy estimated by the first-principles calculation, are built into the diffusion rate model, and the model is applied to the evaluation of the P GB segregation. Since the amount of V is affected by temperature, we evaluated the P GB segregation by the model. As a result, although the model could not simulate the increase of P GB segregation in the high temperature region which is shown by the McLean's diffusion model, the model incorporating the process of capturing and releasing P at GB simulated the increase. Hence, such a process is significant for simulating the temperature dependence.
Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
no journal, ,
For engineering design of deuteron accelerator neutron sources, accurate nuclear data of deuteron-induced reactions on neutron converter (Li, Be, C, etc.) and accelerator structure material (Fe, Cr, Ni, etc.) are indispensable. Therefore we have developed a computational code system based on physics models dedicated for deuteron nuclear data evaluation. In the present study, the code system has been applied to analyses of  reactions on beryllium. Applicability of the code system to deuteron-induced neutron production were examined by comparing calculated Thick Target Yield (TTY) with the experimental ones. As the result of analyses, calculation well reproduced the experimental TTY and applicability of the code system to deuteron-induced neutron production were validated.
reactions on beryllium. Applicability of the code system to deuteron-induced neutron production were examined by comparing calculated Thick Target Yield (TTY) with the experimental ones. As the result of analyses, calculation well reproduced the experimental TTY and applicability of the code system to deuteron-induced neutron production were validated.
Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
no journal, ,
In the present study, we have analyzed the  reactions on beryllium at incident deuteron energies up to 65 MeV using a computational code system dedicated for deuteron nuclear data evaluation we have developed so far. The calculation results with the present code system reproduced the experimental data better than those of PHITS, which is the Monte Carlo particle transport calculation code, especially in high emission energy range. On the other hand, in the low emission energy range, the present calculation cannot reproduce the experimental data well. Therefore, it is necessary to study the contribution from particle emissions from discrete states using the sequential decay model in order to improve the calculation code system.
reactions on beryllium at incident deuteron energies up to 65 MeV using a computational code system dedicated for deuteron nuclear data evaluation we have developed so far. The calculation results with the present code system reproduced the experimental data better than those of PHITS, which is the Monte Carlo particle transport calculation code, especially in high emission energy range. On the other hand, in the low emission energy range, the present calculation cannot reproduce the experimental data well. Therefore, it is necessary to study the contribution from particle emissions from discrete states using the sequential decay model in order to improve the calculation code system.
 iron using kinetic Monte Carlo based on first-principles calculation
iron using kinetic Monte Carlo based on first-principles calculationEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Yamaguchi, Masatake
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Araki, Shohei*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*
no journal, ,
Theoretical model analysis of deuteron-induced activation cross sections were performed using the calculation code system we have developed so far. In our previous works, we analyzed mainly double differential cross sections for the 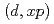 and
and  reactions, and activation cross sections from the
reactions, and activation cross sections from the 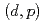 reactions in order to validate calculation method for the direct processes. In the present work, we analyzed activation cross sections from multi particle emission induced by high energy deuteron in order to validate calculation method for statistical decay processes. In the result of analysis, it was found out the calculation method adopted in our code system is valid.
reactions in order to validate calculation method for the direct processes. In the present work, we analyzed activation cross sections from multi particle emission induced by high energy deuteron in order to validate calculation method for statistical decay processes. In the result of analysis, it was found out the calculation method adopted in our code system is valid.
Sadamatsu, Hiroki*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Araki, Shohei*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
no journal, ,
102-MeV deuteron-induced neutron production reactions on Li, Be, C, Al, Cu, Nb are calculated with DEURACS, which is a code system dedicated to deuteron-induced reactions. The calculation results are compared with the latest experimental data and the applicability of DEURACS to deuteron-induced neutron production reactions at around 100 MeV are investigated. As a result, the calculation using DEURACS reproduced experimental double-differential neutron production cross sections and its applicability to the reactions are validated.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Furutachi, Naoya; Iwamoto, Osamu; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
no journal, ,
In the ImPACT project, deuteron is a first candidate of incident beam for nuclear transmutation of long-lived fission products (LLFPs) and accurate deuteron nuclear data on LLFPs are strongly required. Thus, we have performed theoretical model analysis of deuteron-induced spallation reactions on LLFP with DEURACS, which is the computational code dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions. Through comparison with measured data and other calculation method, the applicability of DEURACS to spallation reactions and the role of breakup processes in the reactions will be discussed.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki; Yamaguchi, Masatake
no journal, ,
Phosphorus (P) atoms bring about grain boundary (GB) embrittlement in steel materials and can influence the rise of ductile-brittle transition temperature in reactor pressure vessel steels. Thus, a rate theory model for analyzing irradiation-induced GB P segregation is developed based on the atomistic processes. So far, we have incorporated the trapping process to the model based on the result of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. However, the conventional model is used for the trapping process. In this study, we simulated the migration of a P atom in a GB. In addition, based on the consideration of the MD results, we modified the de-trapping model and applied the rate theory model to the temperature dependence of irradiation-induced GB P segregation. It was found that P atoms migrate through a gap in the GB region. In the calculated GB P segregation, the GB P coverage increased at T  600
600 C and that the increase depended on the GB P segregation energy.
C and that the increase depended on the GB P segregation energy.